글로벌 연구동향
핵의학
- [Clin Nucl Med.] FDG PET으로 폐암예후예측 향상Pretreatment Tumor 18F-FDG Uptake Improves Risk Stratification Beyond RECIST 1.1 in Patients With Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: FDG Uptake and Risk Stratification.
성균관의대 / 문승환, 최준영*, 안명주*
- 출처
- Clin Nucl Med.
- 등재일
- 2019 Feb
- 저널이슈번호
- 44(2):e60-e67. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000002394.
- 내용
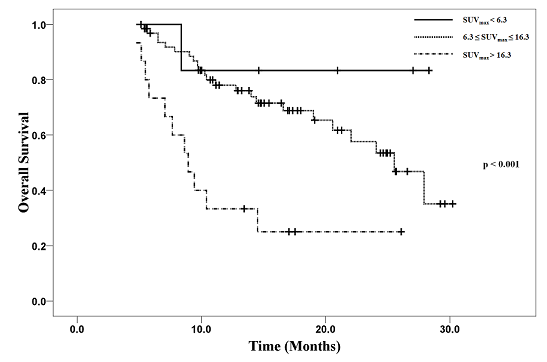

Kaplan-Meier curve of overall survival stratified by SUVmaxin subjects with partial response according to RECIST1.1 (A) and in subjects with stable disease according to RECIST1.1 (B).
Abstract
PURPOSE:
This study investigated the prognostic role of tumor F-FDG uptake on pretreatment scans as an independent indicator and whether its addition improves risk prediction from Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors Version 1.1 (RECIST 1.1).METHODS:
We measured the SUVmax of the most F-FDG-avid tumor lesions on pretreatment scans from 222 patients (age, 60.5 ± 9.5 years; males, 55.2%) with advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer who were enrolled in a prospective phase II clinical trial. We then examined the prognostic value of SUVmax compared with other clinical factors, including chemotherapy response according to RECIST 1.1 criteria.RESULTS:
A multivariable Cox proportional hazards model revealed that an SUVmax greater than 16.3 was an independent predictor of poor progression-free survival (hazards ratio, 3.50; 95% confidence interval, 1.89-6.51; P < 0.000) and overall survival (hazards ratio, 6.87; 95% confidence interval, 2.51-18.76; P < 0.000), whereas RECIST 1.1 did not show a significant association with any survival outcome. Furthermore, improvement was achieved by adding SUVmax to RECIST 1.1, which increased the net reclassification index (27.4%; P = 0.046) and integrated discrimination improvement (integrated discrimination improvement, 10.6%; P = 0.026). Similarly, adding RECIST 1.1 to SUVmax also improved net reclassification index (68.9%, P = 0.006) and integrated discrimination improvement (25.4%, P = 0.006) for prognosis prediction.CONCLUSIONS:
High tumor F-FDG uptake on a pretreatment scan is an independent prognostic indicator that can significantly improve risk stratification when added to RECIST 1.1 for patients with advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer.
Author informationMoon SH1, Sun JM2, Ahn JS2, Park K2, Ahn MJ2, Choi JY1.
1
From the Department of Nuclear Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, and.
2
Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea.
- 연구소개
- 현재 진행성 비소세포폐암의 항암치료에 대한 반응 평가는 CT 영상에서의 크기 변화를 바탕으로 하는 RECIST(Response evaluation criteria in solid tumors) criteria가 기본적으로 사용되고 있으나 여러 가지 문제점들을 지니고 있습니다. FDG PET은 종양 치료 반응 평가에 유용하며 RECIST 평가 방식에 문제점을 보완하여 보다 정확하고 세밀한 치료 반응 평가를 가능하게 할 것으로 기대되나 아직까지 RECIST를 대치하지는 못하고 있는 상황입니다. 이번 연구의 결과는 진행성 비소세포폐암에서 치료 전 종양의 FDG 섭취 정도가 환자의 예후와 유의한 연관이 있으며, 치료 반응 평가에 RECIST criteria를 보완할 수 있음을 보이고 있습니다. PET을 이용한 종양반응평가에 관심이 많은 임상연구자들에게 도움이 될 만한 좋은 연구라 생각합니다.
- 덧글달기










편집위원
폐암환자의 FDG PET 영상에서 구한 파라미터 중 가장 보편적으로 이용되는 SUV가 진행된 비편평세포 폐암의 위험성 분류에 독립적인 예후 인자임을 보여준 임상 연구임. 해당 연구 결과는 핵의학 영상분석 관심 연구자, 종양학 및 호흡기학 임상 의사들에게 관심을 끌 수 있는 연구로 보임.
2019-03-14 14:12:50