글로벌 연구동향
핵의학
- [J Nucl Med.] Whole-Body Voxel-Based Personalized Dosimetry: The Multiple Voxel S-Value Approach for Heterogeneous Media with Nonuniform Activity Distributions.
서울의대, 한국표준과학연구원 / 이민선, 이재성*, 김중현*
- 출처
- J Nucl Med.
- 등재일
- 2018 Jul
- 저널이슈번호
- 59(7):1133-1139. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.117.201095. Epub 2017 Dec 14.
- 내용
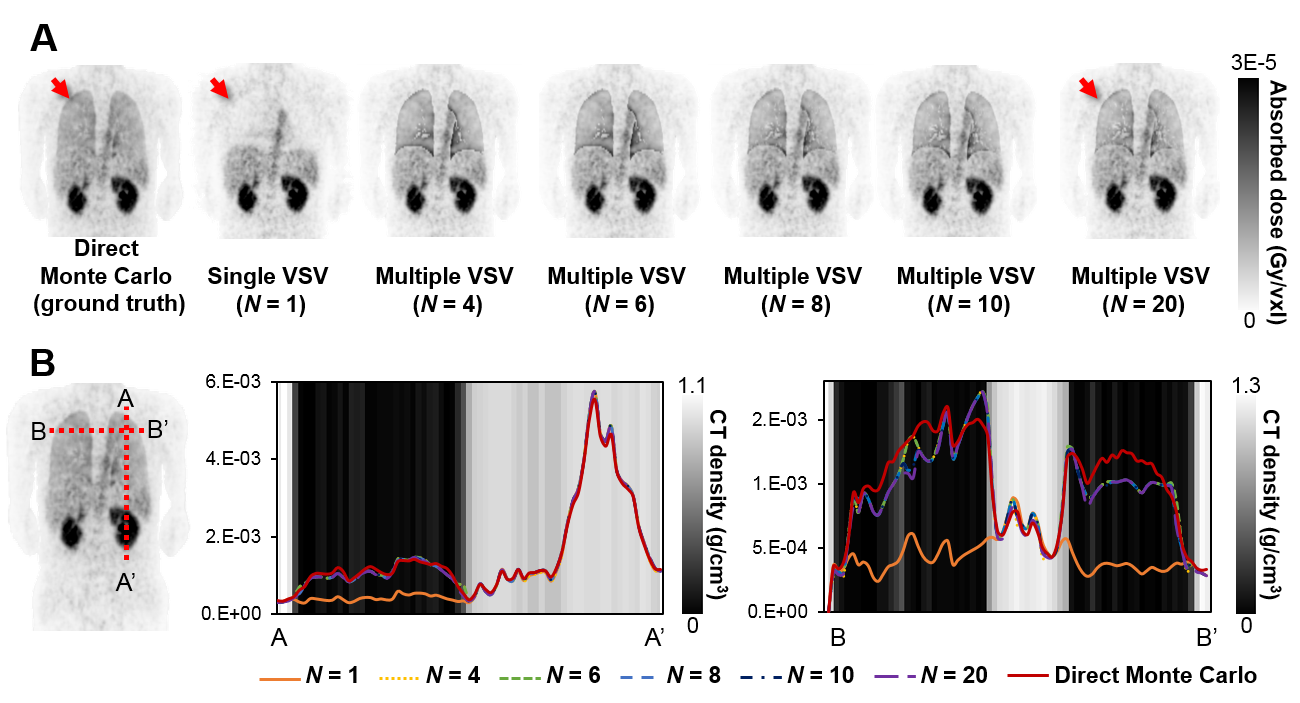
A. 몬테카를로 시뮬레이션 (ground truth), 기존의 voxel S-value 기법 (N=1), 본 연구에서 제안된 multiple voxel S-value 기법 (N=4, 6, 8, 10, 20)을 통하여 획득한 선량분포 맵.
B. 각 선량평가기법에 대한 선량 프로파일.
본 논문에서 제안한 방법이 기존의 기법에 비해 ground truth와 더 유사한 선량분포맵을 보이는 것을 확인할 수 있었습니다.
Abstract
Personalized dosimetry with high accuracy is becoming more important because of the growing interest in personalized medicine and targeted radionuclide therapy. Voxel-based dosimetry using dose point kernel or voxel S-value (VSV) convolution is available. However, these approaches do not consider the heterogeneity of the medium. Here, we propose a new method for whole-body voxel-based personalized dosimetry in heterogeneous media with nonuniform activity distributions-a method we refer to as the multiple VSV approach. Instead of using only a single VSV, as found in water, the method uses multiple numbers (N) of VSVs to cover media of various density ranges, as found in the whole body. Methods: The VSVs were precalculated using GATE Monte Carlo simulation and were convoluted with the time-integrated activity to generate density-specific dose maps. CT-based segmentation was performed to generate a binary mask image for each density region. The final dose map was acquired by the summation of N segmented density-specific dose maps. We tested several sets of VSVs with different densities: N = 1 (single water VSV), 4, 6, 8, 10, and 20. To validate the proposed method, phantom and patient studies were conducted and compared with the direct Monte Carlo approach, which was considered the ground truth. Finally, dosimetry on 10 patients was performed using the multiple VSV approach and compared with the single VSV and organ-based approaches. Errors at the voxel and organ levels were reported for 8 organs. Results: In the phantom and patient studies, the multiple VSV approach showed significant decreases in voxel-level errors, especially for the lung and bone regions. As the number of VSVs increased, voxel-level errors decreased, although some overestimations were observed at the lung boundaries. For the multiple VSVs (N = 8), we achieved a voxel-level error of 2.06%. In the dosimetry study, our proposed method showed greatly improved results compared with single VSV and organ-based dosimetry. Errors at the organ level were -6.71%, 2.17%, and 227.46% for single VSV, multiple VSV, and organ-based dosimetry, respectively. Conclusion: The multiple VSV approach for heterogeneous media with nonuniform activity distributions offers fast personalized dosimetry at the whole-body level, yielding results comparable to those of the direct Monte Carlo approach.
Author informationLee MS1,2, Kim JH3, Paeng JC1, Kang KW1,4, Jeong JM1,2,4, Lee DS1, Lee JS5,2,4.
1
Department of Nuclear Medicine, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
2
Interdisciplinary Program in Radiation Applied Life Science, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
3
Center for Ionizing Radiation, Korea Research Institute of Standards and Sciences, Daejeon, Korea; and jaes@snu.ac.kr kimjh14@kriss.re.kr.
4
Department of Biomedical Sciences, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
5
Department of Nuclear Medicine, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea jaes@snu.ac.kr kimjh14@kriss.re.kr.http://www.rmwebzine.re.kr/newshome/mtnmain.php?mtnkey=articleview&mkey=scatelist&mkey2=76&aid=2754
- 키워드
- Monte Carlo simulation; heterogeneous medium; radiation dosimetry; voxel S value
- 연구소개
- 최근 핵의학 영상에서 환자 개개인의 선량평가를 (personalized dosimetry) 통한 치료 효과 및 risk-benefit 분석이 매우 중요해지고 있습니다. 현재 가장 널리 사용되고 있는 선량평가법인 voxel S-value 나 dose point kernel 방법은 인체 내 조직 및 장기의 비균일도를 고려하지 못한다는 단점이 있습니다. 몬테카를로 시뮬레이션 기반의 선량평가법은 현재 가장 정확하다고 알려져 있으나, 복셀 수준의 선량 계산 속도가 매우 오래 걸리므로 현실적으로 임상에 적용하는 데에는 아직 한계가 있습니다. 이에 따라 본 논문에서는 기존의 방법들의 한계를 극복한 새로운 복셀 기반 선량평가기법인 “multiple voxel S-value approach”를 제안하였습니다. 제안한 방법은 인체 내 조직들의 밀도 영역에 해당하는 다 수의 voxel S-value들을 이용하여 whole-body 수준에서 선량을 계산할 수 있는 알고리즘을 제안하였습니다. 본 논문에서 제안된 방법은 환자 내의 불균일한 선량 및 조직 분포를 모두 고려 가능한 personalized dosimetry 기법으로 환자 개개인의 흡수선량을 빠른 시간 내에 정확하게 계산 가능하다는 장점이 있습니다.
- 덧글달기









