글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
- 2024년 05월호
[Radiother Oncol .] Risk of clinically significant cardiovascular disease associated with postoperative radiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving surgical resection followed by adjuvant chemotherapy: A Korean nationwide cohort study서울의대 / 권진이, 김병혁*
- 출처
- Radiother Oncol .
- 등재일
- 2024 Mar 24:195:110241. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2024
- 저널이슈번호
- 내용
Abstract
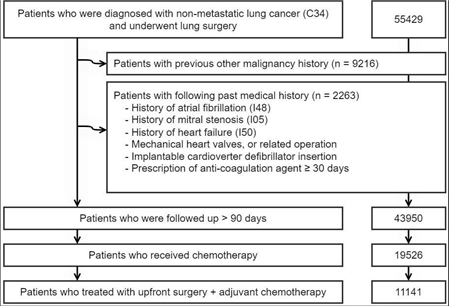
Background: There are no large-scale datasets that analyze the relationship between postoperative radiotherapy (PORT) and various cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) in patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Therefore, we aimed to investigate the incidences of CVDs with PORT using a national population-based database.Methods: Patients diagnosed with NSCLC who underwent curative surgery followed by adjuvant chemotherapy were included from 2007 to 2017. Patients with a prior diagnosis of heart failure (HF), atrial fibrillation (AFib), or heart surgery were excluded. A total of 11,141 patients were included in the final analysis. PORT was used in 1334 patients. Most patients received lobectomy with mediastinal lymph node dissection.
Results: Major adverse cardiac events mostly occurred within 3-4 years from the diagnosis. After the median follow-up duration of 70.6 months, HF was the most diagnosed disease (5.3 %), followed by AFib (4.5 %), stroke (4.1 %), and pulmonary embolism (3.5 %). All the incidences of clinically significant CVDs did not differ by PORT. This result remained unchanged after the propensity score matching comparison. Age ≥ 65, underlying hypertension, and history of ischemic heart disease were the most related factors to the occurrence of HF and AFib. No significant difference in CVD-free survivals according to PORT status was observed. When stratified by proposed scoring, there were no subgroups showed increased incidence by PORT.
Conclusions: These results suggest that PORT had no significant impact on various CVD occurrences in NSCLC patients without underlying heart disease.
Affiliations
Jeanny Kwon 1, Byoung Hyuck Kim 2
1Department of Radiation Oncology, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Munhwa-ro 282, Jung-gu, Daejeon 35015, Republic of Korea.
2Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, 20, Boramae-ro 5-gil, Dongjak-gu, Seoul 07061, Republic of Korea. Electronic address: karlly71@snu.ac.kr.
- 키워드
- Cardiovascular disease; Non-small cell lung cancer; Postoperative radiotherapy.
- 연구소개
- 폐암의 수술후 방사선치료 (PORT) 결정에 영향을 주는 요소 중 cardiovascular toxicity 에 대해 national population-based database 수준에서 근거를 제시하고자 수행된 연구입니다. 결론적으로 나이, 고혈압, 허혈성심장병이 가장 중요한 독성예측인자였으며, 방사선치료는 통계적으로 유의한 차이를 만들지 않았습니다. 국내에서 대규모 환자군 대상으로 분석된 데이터인만큼, PORT 권고 및 환자선택에 고려할 수 있는 참고자료가 될것으로 생각합니다.
- 덧글달기








편집위원
비소세포폐암환자에서 수술후 방사선치료(PORT)가 향후 심장혈관질환 발생의 위험도를 증가시킬 수 있다는 것은 논란의 여지가 있는 상황에서 본 연구는 심평원 데이터(HIRA)를 이용한 대규모 환자를 분석한 연구로, 분석 결과 PORT가 심장혈관질환에 유의미한 영향을 보이지 않는 것으로 결론냄.
덧글달기닫기2024-05-03 10:59:59
등록
편집위원3
본 논문은 기존에 확인된 바 없는 수술 후 adjuvant chemotherapy를 받는 비소세포성 폐암(NSCLC) 환자의 postoperative radiotherapy (PORT)와 다양한 심혈관 질환 (CVD) 사이의 관계를 국내에서 코호트를 대규모로 분석했다.
본 연구를 통해서 PORT가 NSCLC 환자의 CVD 발생에 영향을 미치지 않음을 확인하였으며, 이 결과를 통해서 NSCLC 환자 또는 의료진이 심혈관계에 미칠 영향을 고려하여 PORT를 선택할 수 있는 유용한 정보를 제공한다는데에 의의가 있다.
덧글달기닫기2024-05-03 14:39:08
등록