글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
- 2019년 05월호
[PLoS One.] Elective pelvic irradiation in prostate cancer patients with biochemical failure following radical prostatectomy: A propensity score matching analysis.서울의대, 울산의대 / 송창훈, 변상준, 김재성*, 김영석*
- 출처
- PLoS One.
- 등재일
- 2019 Apr 11
- 저널이슈번호
- 14(4):e0215057. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215057. eCollection 2019.
- 내용
Abstract
PURPOSE:
To investigate whether whole pelvic radiotherapy (WPRT) improves biochemical relapse-free survival (bRFS) vs. prostate bed radiotherapy (PBRT) in prostate cancer patients receiving salvage radiotherapy (SRT) after radical prostatectomy.METHODS:
Data from patients with prostate cancer who underwent SRT for biochemical recurrence between 2005 and 2012 in two academic institutions were retrospectively reviewed. Patients treated with WPRT in one hospital were compared with patients treated with PBRT in the other. Propensity scoring was performed to balance the characteristics of the different treatment groups, and bRFS was compared.RESULTS:
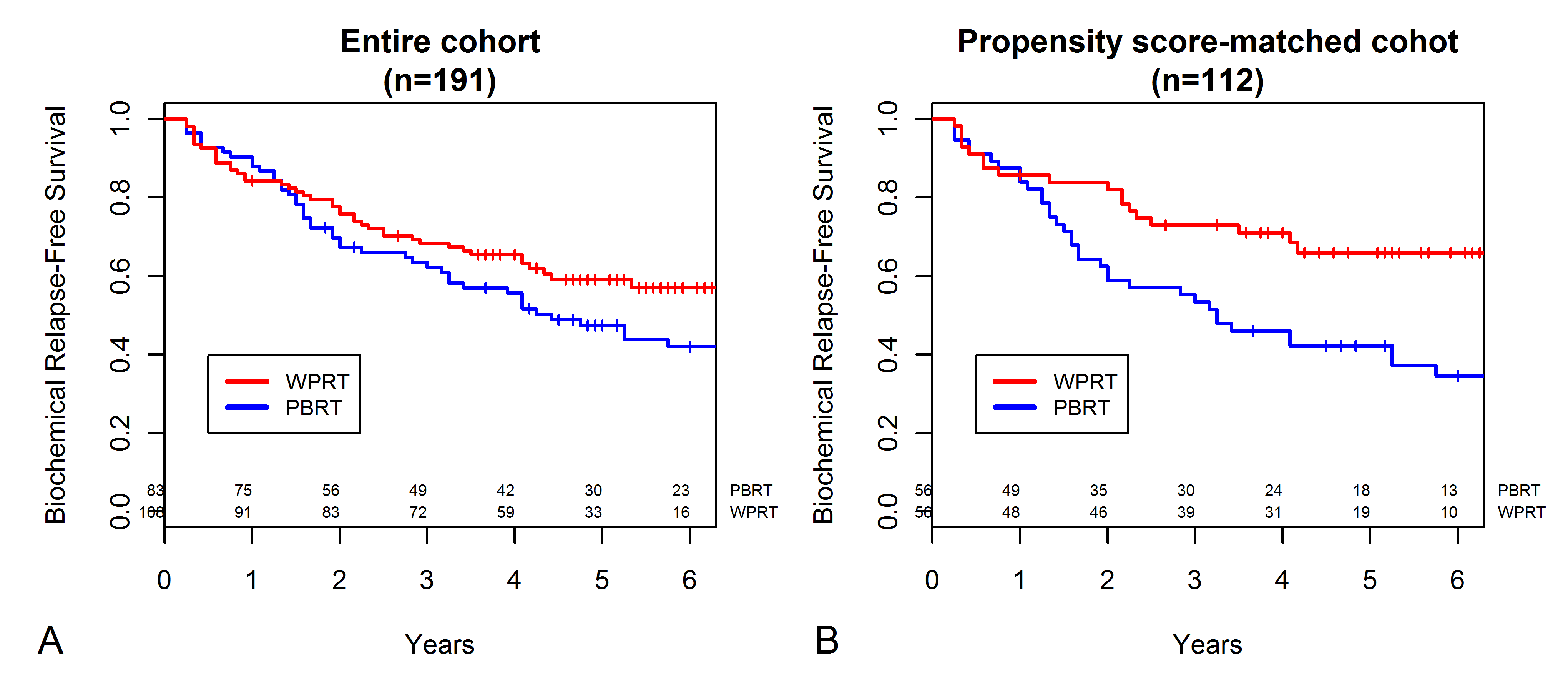
Data from a total of 191 patients were included in the analysis (WPRT, n = 108; PBRT, n = 83). The median follow-up period was 66 months. Prior to matching, patients who received WPRT had higher pathologic Gleason scores as well as a higher incidence of pre-SRT PSA levels >0.5 ng/mL and lower rates of concurrent androgen-deprivation therapy. Propensity score matching balanced these characteristics and generated a cohort comprising 56 patients from each group. In the matched cohort, the 5 year bRFS of the WPRT group was significantly higher than that of the PBRT group (65.9 vs. 42.2%, p = 0.017). Multivariate analysis revealed that WPRT was an independent prognostic factor for bRFS (hazard ratio: 0.45, 95% confidence interval: 0.26-0.75, p = 0.002). This benefit of WPRT on bRFS was maintained in subgroup analyses, especially in patients with preoperative PSA level ≤20 ng/mL or pre-SRT PSA level ≥0.4 ng/mL.CONCLUSIONS:
These data suggest that, following radical prostatectomy, elective WPRT during SRT may improve bRFS compared with PBRT in selected patients. Patients with preoperative PSA level ≤20 ng/mL or pre-SRT PSA level ≥0.4 ng/mL represent a potential subgroup who benefit most from receiving WPRT. Results of prospective randomized trials are awaited to confirm this finding.
Author informationSong C1, Byun SJ2, Kim YS3, Ahn H4, Byun SS5, Kim CS4, Lee SE5, Kim JS1.
1
Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Republic of Korea.
2
Department of Radiation Oncology, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Republic of Korea.
3
Department of Radiation Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
4
Department of Urology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
5
Department of Urology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Republic of Korea.
- 연구소개
- 전립선 적출술 후 PSA가 상승할 경우 유일한 근치적 치료로서 방사선치료를 시행하게 됩니다. 현재까지의 표준은 전립선 수술부위(prostate bed)에 2 Gy 씩 33회 총 66 Gy의 방사선치료를 하는 것입니다. 전립선 수술부위 뿐만 아니라 골반림프절을 포함하는 것에 대해서는 현재 그 역할이 증명되어있지 않습니다. 본 연구에서는 치료 방침이 서로 다른 두 병원에서 각각 전립선 수술부위에만/전립선수술부위+골반림프절에 대한 방사선치료를 시행한 임상결과를 후향적으로 성향점수를 일치시켜 분석하였습니다. 결과로서 전골반림프절을 방사선치료 범위에 포함시켰을 때 치료성적의 상승(biochemical recurrence free survival)을 관찰할 수 있었습니다. 후향적 연구의 한계를 고려하여 추후 전향적 연구결과를 기다려봐야 하겠습니다.
- 덧글달기








편집위원
수술 후 PSA failure가 발생한 prostate cancer 환자에서 whole pelvic radiotherapy로 benefit을 얻을 수 있는 subgroup을 제시하였다는 점에서 임상진료시 도움이 될 것으로 생각됩니다.
덧글달기닫기2019-05-28 17:29:48
등록