글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
- [Cancer Res Treat.] The Prognostic Impact of the Number of Metastatic Lymph Nodes and a New Prognostic Scoring System for Recurrence in Early-Stage Cervical Cancer with High Risk Factors: A Multicenter Cohort Study (KROG 15-04).
분당서울대병원 / 권진이, 엄근용*
- 출처
- Cancer Res Treat.
- 등재일
- 2018 Jul
- 저널이슈번호
- 50(3):964-974. doi: 10.4143/crt.2017.346. Epub 2017 Oct 24.
- 내용
Abstract
Purpose:
We aimed to assess prognostic value of metastatic pelvic lymph node (mPLN) in early-stage cervical cancer treated with radical surgery followed by postoperative chemoradiotherapy. Also, we sought to define a high-risk group using prognosticators for recurrence.Materials and Methods:
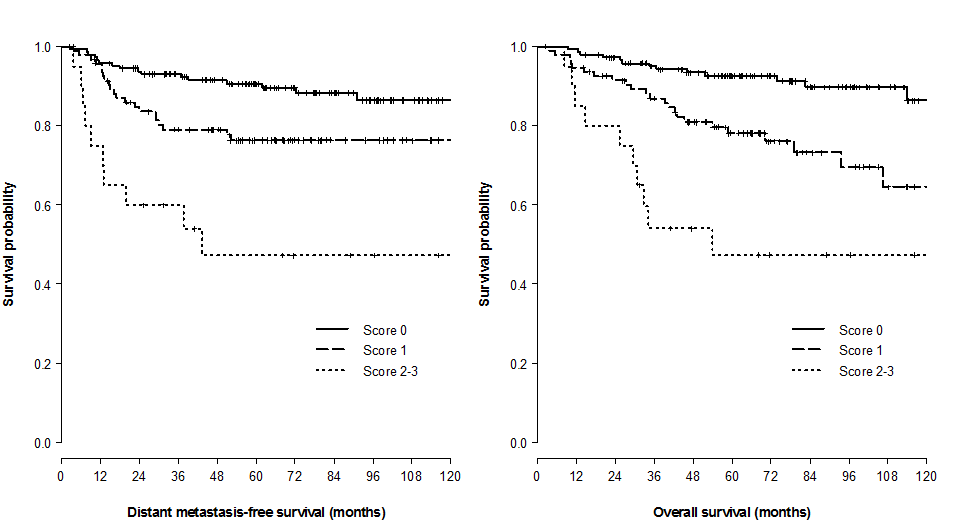
A multicenter retrospective study was conducted using the data from 13 Korean institutions from 2000 to 2010. A total of 249 IB-IIA patients with high-risk factors were included. We evaluated distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS) and disease-free survival (DFS) in relation to clinicopathologic factors including pNstage, number of mPLN, lymph node (LN)ratio (number of positive LN/number of harvested LN), and log odds of mPLNs (log(number of positive LN+0.5/number of negative LN+0.5)).Results:
In univariate analysis, histology (squamous cell carcinoma [SqCC] vs. others), lymphovascular invasion (LVI), number of mPLNs (≤ 3 vs. > 3), LN ratio (≤ 17% vs. > 17%), and log odds of mPLNs (≤ -0.58 vs. > -0.58) were significant prognosticators for DMFS and DFS. Resection margin involvement only affected DFS. No significant survival difference was observed between pN0 patients and patients with 1-3 mPLNs. Multivariate analysis revealed that mPLN > 3, LVI, and non-SqCC were unfavorable index for both DMFS (p < 0.001, p=0.020, and p=0.031, respectively) and DFS (p < 0.001, p=0.017, and p=0.001, respectively). A scoring system using these three factors predicts risk of recurrence with relatively high concordance index (DMFS, 0.69; DFS, 0.71).Conclusion:
mPLN > 3 in early-stage cervical cancer affects DMFS and DFS. A scoring system using mPLNs > 3, LVI, and non-SqCC could stratify risk groups of recurrence in surgically resected early-stage cervix cancer with high-risk factors.
Author informationKwon J1, Eom KY2, Kim YS3, Park W4, Chun M5, Lee J6, Kim YB7, Yoon WS8, Kim JH9, Choi JH10, Chang SK11, Jeong BK12, Lee SH13, Cha J14.
1
Department of Radiation Oncology, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
2
Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
3
Department of Radiation Oncology, Asan Medical center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
4
Department of Radiation Oncology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
5
Department of Radiation Oncology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
6
Department of Radiation Oncology, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
7
Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei Cancer Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
8
Department of Radiation Oncology, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Korea.
9
Department of Radiation Oncology, Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
10
Department of Radiation Oncology, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
11
Department of Radiation Oncology, CHA Bundang Medicial Center, CHA University School of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
12
Department of Radiation Oncology, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea.
13
Department of Radiation Oncology, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Incheon, Korea.
14
Department of Radiation Oncology, Wonju Severance Christian Hospital, Wonju, Korea.
- 키워드
- Adjuvant treatment; Combined modality therapy; Lymphatic metastasis; Scoring system; Uterine cervical neoplasms
- 연구소개
- 조기 자궁경부암에서 골반 림프절의 침범여부는 수술 이후에 추가적인 치료방법 결정에 영향을 미치는 중요한 예후인자입니다. 그러나 얼마만큼의 림프절을 침범해야 환자들의 예후에 의미있는 영향을 미칠 것인가에 대해서는 아직 잘 밝혀져있지 않았습니다. 본 연구에서는 해당 환자들을 다양한 인자를 이용하여 분류하고 예후를 예측할 수 있는 방법을 제시하였습니다. 예후가 좋을 것으로 예상되는 환자군에서 과잉치료를 피하고, 반대로 예후가 좋지 않을 것으로 예상되는 환자군에서 새로운 치료방법을 모색하는 데에 도움이 될 수 있을 것으로 생각합니다.
- 덧글달기









